Type of structure and the support configuration of offshore platform are in consideration with depth and difficulties in erecting the platform. Therefore, there are many types of offshore platform. Based on the type of structure, offshore platform can be divided as :
- Concrete gravity platform
- Fixed steel platform
- Semi submersible platform
- Tension leg platform
- Guyed tower platform

A ‘Statfjord’ gravity based structure under construction in Norway.
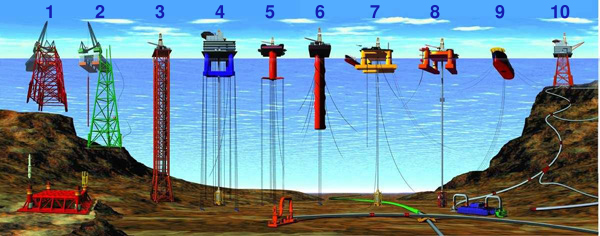 1, 2) conventional fixed platforms; 3) compliant tower; 4, 5) vertically moored tension leg and mini-tension leg platform; 6) Spar ; 7,8) Semi-submersibles ; 9) Floating production, storage, and offloading facility; 10) sub-sea completion and tie-back to host facility.
1, 2) conventional fixed platforms; 3) compliant tower; 4, 5) vertically moored tension leg and mini-tension leg platform; 6) Spar ; 7,8) Semi-submersibles ; 9) Floating production, storage, and offloading facility; 10) sub-sea completion and tie-back to host facility.In addition to that classification, depending on the number of legs & jacket type, fixed offshore platform can be divided into :
- Monopod platform
- Bipod platform
- Tripod platform
- 4, 6, or 8 pile platform
In a common Offshore platform, deck, jacket, and pile are fabricated onshore. The first stage of platform erection is transporting the jacket and putting it in the designated place. After the jacket is fixed in the right place, pile is driven via the jacket hollow tube to the sea bed. Finally, the deck part is placed and connected at the top of support structure.
For safety and ergonomic reasons, platform layout should be carefully designed. Platform north should be facing to deeper water. This north part is also used as the area for jack up drilling rig and foundations spud can or mat. The south side platform is used for boat berthing, pipeline riser and subsea pipeline. Layout of platform should also be designed by considering drilling sequence, prevailing wind, and other utility such as helipad.
Load acting on platform is vital in a platform’s design stage. In designing a platform, load can be divided to load at deck structure and load at jacket structure. In general, the working load in an offshore platform consisted of the following load.
Load at Deck structure:
- Topside load : Deck structure, piping, equipment, life load, crane load, helicopter load, drilling work over load.
- Lateral load : Wind and earthquake.
- Vertical load : Deck structure and buoyancy
- Lateral load : Wind, wave, current, earthquake, and added hydrodynamic mass.
- API RP2A Recommended Practice for Planning, Designing and Constructing Fixed Offshore Platforms
- AISC Specifications for Design, Fabrication and Erection of Structural Steel Buildings
- API Spec 2B, Fabricated Structural Pipes
- AWS D 1.1, section 8 and 10
- ISO 19902 Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries – Fixed Steel Offshore Structures
- ISO 19901-2 Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries – Specific requirements for offshore structures Part 2 Seismic Design Procedures and Criteria
